Introduction in Empower Your Mind and Body
Exercise is one of the most important things you can do for your health and well-being. It can help you prevent and manage various chronic diseases, improve your mood and cognition, and enhance your quality of life. But not all exercises are created equal. There are different types of exercise that target different aspects of your fitness, such as your cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, and balance. By understanding the different types of exercise and how they Empower Your Mind and Body, you can design a workout routine that suits your needs and goals.
In this article, we will explain the four main types of exercise: aerobic, anaerobic, flexibility, and balance. We will also discuss the benefits of exercise for your physical and mental health, and provide some tips on how to create a balanced and effective workout routine. Whether you are a beginner or an expert, this article will help you empower your mind and body with exercise.
Also read: Eisenhower Matrix: Your Ultimate Time Management Hack » Upgrade Your Life (lifeupgrad.com)
Types of Exercise
Exercise can be classified into four main categories, depending on how it Empower Your Mind and Body’s energy systems, oxygen consumption, and muscle contraction. These are:
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, is any activity that increases your heart rate and breathing for a sustained period of time. It involves using oxygen to produce energy for your muscles. Some examples of aerobic exercise are:
- Running
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Rowing
- Dancing
- Hiking
- Skipping
Aerobic exercise improves your cardiovascular endurance, which is your ability to perform moderate to vigorous physical activity for a long time without getting tired. It also strengthens your heart, lungs, and blood vessels, and lowers your blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Aerobic exercise can help you burn calories and lose weight, as well as reduce your risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and some cancers.
Anaerobic Exercise
Anaerobic exercise, also known as strength training, is any activity that involves short bursts of intense effort that exceed your oxygen supply. It involves using stored energy sources, such as glucose and creatine phosphate, to power your muscles. Some examples of anaerobic exercise are:
- Lifting weights
- Sprinting
- Jumping
- Climbing
- Push-ups
- Pull-ups
- Squats
Anaerobic exercise improves your muscular strength, which is your ability to exert force against resistance. It also increases your muscle mass, bone density, and metabolism, and helps you maintain a healthy body composition. Anaerobic exercise can help you prevent and treat osteoporosis, arthritis, back pain, and obesity. It can also improve your posture, balance, and coordination.
Flexibility Exercise
Flexibility exercise, also known as stretching, is any activity that increases the range of motion of your joints and muscles. It involves gently lengthening and relaxing your muscles and connective tissues. Some examples of flexibility exercise are:
- Yoga
- Pilates
- Tai chi
- Ballet
- Static stretching
- Dynamic stretching
- Foam rolling
Flexibility exercise improves your mobility, which is your ability to move your joints and muscles through their full potential. It also reduces muscle tension, stiffness, and soreness, and improves your blood circulation and joint lubrication. Flexibility exercise can help you prevent and recover from injuries, improve your performance in other types of exercise, and enhance your relaxation and stress management.
Balance Exercise
Balance exercise, also known as stability training, is any activity that challenges your ability to maintain your center of gravity and posture. It involves engaging your core muscles and using your sensory feedback from your eyes, ears, and skin. Some examples of balance exercise are:
- Standing on one leg
- Walking on a narrow beam
- Standing on a wobble board
- Performing a single-leg squat
- Doing a plank
- Playing catch
- Riding a bike
Balance exercise improves your stability, which is your ability to control your body’s position and movement. It also improves your agility, which is your ability to change direction and speed quickly and efficiently. Balance exercise can help you prevent falls and injuries, especially as you age. It can also improve your confidence, coordination, and reaction time.
Benefits of Exercise and Empower Your Mind and Body
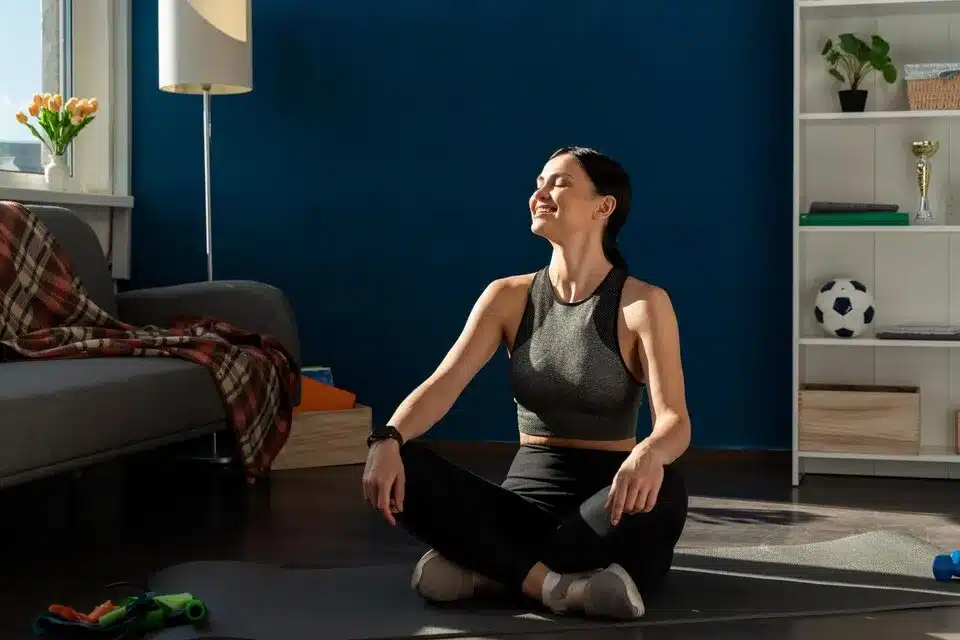

Exercise is not only good for your body, but also for your mind. It can provide a range of benefits for your physical and mental health, such as:
Physical Benefits
- Improves your cardiovascular health and reduces your risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
- Enhances your respiratory health and reduces your risk of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and lung cancer
- Boosts your immune system and reduces your risk of infections, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases
- Regulates your blood sugar levels and reduces your risk of diabetes and metabolic syndrome
- Supports your digestive health and reduces your risk of constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and colorectal cancer
- Promotes your bone health and reduces your risk of osteoporosis, fractures, and falls
- Strengthens your muscles and joints and reduces your risk of arthritis, back pain, and muscle loss
- Maintains your body weight and composition and reduces your risk of obesity and eating disorders
- Prevents and manages various chronic diseases, such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis
- Increases your lifespan and reduces your risk of premature death
Mental Benefits
- Improves your mood and reduces your risk of depression, anxiety, and mood disorders
- Enhances your cognition and reduces your risk of dementia, cognitive decline, and memory loss
- Stimulates your creativity and problem-solving skills and improves your learning and academic performance
- Boosts your self-esteem and confidence and improves your body image and self-acceptance
- Relieves your stress and tension and improves your coping and resilience skills
- Increases your motivation and energy and improves your productivity and work performance
- Fosters your social skills and relationships and reduces your risk of loneliness and isolation
- Provides you with fun and enjoyment and improves your quality of life and happiness
How to Create a Workout Routine
Now that you know the different types of exercise and their benefits, you might be wondering how to create a workout routine that works for you to Empower Your Mind and Body. Here are some steps you can follow to design a balanced and effective workout routine:
Assess Your Fitness Level and Goals
Before you start exercising, you need to assess your current fitness level and determine your goals. You can do this by:
- Measuring your height, weight, body mass index, body fat percentage, and waist circumference
- Testing your cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, and balance
- Evaluating your medical history, health conditions, injuries, and medications
- Identifying your reasons, interests, preferences, and expectations for exercising
- Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your fitness outcomes
Choose the Right Exercises for You
Once you have assessed your fitness level and goals, you need to choose the right exercises for you. You can do this by:
- Selecting a variety of exercises that cover all four types of exercise: aerobic, anaerobic, flexibility, and balance
- Choosing exercises that match your fitness level, goals, interests, and preferences
- Considering your equipment, space, time, and budget availability
- Consulting a fitness professional, such as a personal trainer, physiotherapist, or exercise physiologist, for guidance and advice
Plan Your Schedule and Frequency
After you have chosen the right exercises for you, you need to plan your schedule and frequency. You can do this by:
- Allocating at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over at least three days
- Performing at least two sessions of anaerobic exercise per week, targeting all major muscle groups, with at least 48 hours of rest between sessions
- Incorporating flexibility exercise into your warm-up and cool-down routines, or doing it separately at least two to three times per week
- Adding balance exercise to your aerobic or anaerobic workouts, or doing it separately at least two to three times per week
- Scheduling your workouts at a time that suits your lifestyle, circadian rhythm, and energy levels
- Balancing your workouts with adequate rest, recovery, and sleep
Track Your Progress and Adjust as Needed
Finally, you need to track your progress and adjust as needed. You can do this by:
- Monitoring your exercise intensity, duration, frequency, and volume
- Recording your exercise performance, such as your speed, distance, repetitions, and weight
- Measuring your fitness outcomes, such as your weight, body fat percentage, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels
- Evaluating your exercise satisfaction, such as your enjoyment, motivation, and confidence
- Adjusting your workout routine as needed, based on your feedback and results
- Celebrating your achievements and rewarding yourself for your efforts
- Seeking social support and accountability from your friends, family, or online communities
- Finding new ways to challenge yourself and keep your workouts fun and interesting
Conclusion
Exercise is a powerful way to empower your mind and body. It can improve your physical and mental health, as well as your quality of life and happiness. By understanding the different types of exercise and how they affect your body and mind, you can create a workout routine that suits your needs and goals. Remember to assess your fitness level and goals, choose the right exercises for you, plan your schedule and frequency, track your progress and adjust as needed, and enjoy the process and the results.
We hope this article has helped you learn more about the types of exercise and how to create a workout routine. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. We would love to hear from you. Thank you for reading and happy exercising! 🏃♂️🏋️♀️🧘♂️🚴♀️
**** Resources to download and listen to free books about: Health and Wellness – search | Open Library
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers about exercise and workout routines:
how Empower Your Mind and Body?
Empowering your mind and body is a transformative journey that can lead to personal growth and well-being. Here are some techniques and practices to help you achieve empowerment:
- Yoga Affirmations:
- Yoga affirmations are a powerful way to nurture your mind, body, and soul simultaneously.
- These positive statements come from various traditions worldwide and can instill happiness, compassion, and peace.
- Incorporate them into your daily routine during yoga sessions or whenever you need a boost.
- Examples of yoga affirmations include:
- “I am strong.”
- “I am capable.”
- Consistency and tailoring the affirmations to your needs are key1.
- Mind-Body Connection:
- Understand the intricate link between your mind and body.
- Practices like mindfulness and meditation can empower you by fostering self-awareness and reducing stress2.
- Self-Help Techniques:
- Explore self-help strategies to transform your life.
- Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and overcoming obstacles play a vital role in personal growth and empowerment2.
- Embrace Freedom with Yoga:
- Yoga not only strengthens your body but also liberates your mind.
- Use affirmations to release emotional limitations and experience greater freedom1.
Remember, empowerment begins within. Cultivate a positive mindset, practice self-care, and explore techniques that resonate with you. 🌟🧘♀️🌿
What is the best time to exercise?
There is no definitive answer to this question, as the best time to exercise depends on your personal preference, lifestyle, and circadian rhythm. Some people prefer to exercise in the morning, as it can help them wake up, boost their metabolism, and set a positive tone for the day. Others prefer to exercise in the evening, as it can help them unwind, relieve stress, and sleep better. The most important thing is to find a time that works for you and stick to it.
How much exercise do I need?
The amount of exercise you need depends on your age, health, and fitness goals. However, as a general guideline, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that adults aged 18 to 64 should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as well as muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week. Older adults aged 65 and above should follow the same recommendations, but also include balance and flexibility exercises to prevent falls and improve mobility.
What are some common exercise myths?
There are many myths and misconceptions about exercise that can hinder your progress and motivation. Here are some of the most common ones and the truth behind them:
- Myth: You need to exercise for at least an hour to see any benefits.
- Truth: Even short bouts of exercise can have positive effects on your health and well-being. According to a study by the American Heart Association, 15 minutes of brisk walking per day can reduce your risk of death by 22%.
- Myth: You can target specific areas of your body to lose fat.
- Truth: You cannot spot-reduce fat from certain parts of your body, such as your belly, thighs, or arms. Fat loss occurs when you burn more calories than you consume, and your body decides where to store and use fat based on your genetics, hormones, and other factors. The best way to lose fat is to combine aerobic and anaerobic exercises with a balanced diet.
- Myth: You need to stretch before you exercise to prevent injuries.
- Truth: Stretching before you exercise can actually increase your risk of injuries, as it can reduce your muscle strength, power, and performance. Instead, you should do a dynamic warm-up, which involves moving your joints and muscles through their full range of motion, such as jogging, skipping, lunging, and swinging. You can do static stretching, which involves holding a position for 10 to 30 seconds, after you exercise, as it can help you relax and improve your flexibility.
How can I stay motivated to exercise?
Staying motivated to exercise can be challenging, especially when you face obstacles, setbacks, or boredom. Here are some tips to help you stay motivated to exercise:
- Set SMART goals and track your progress
- Celebrate your achievements and reward yourself for your efforts
- Seek social support and accountability from your friends, family, or online communities
- Find new ways to challenge yourself and keep your workouts fun and interesting



I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?